How Big Was Tyrannosaurus?

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
Tyrannosaurus Rex was one of the largest land carnivores of all time. Adults typically measured up to 42 feet (12.8 meters) in length, stood about 15 to 20 feet (4.6 to 6 meters) tall at the hips, and weighed an estimated 5 to 7 tons, with some studies suggesting even heavier individuals. Its massive skull alone could be over 5 feet long.
How Did Tyrannosaurus Hunt?
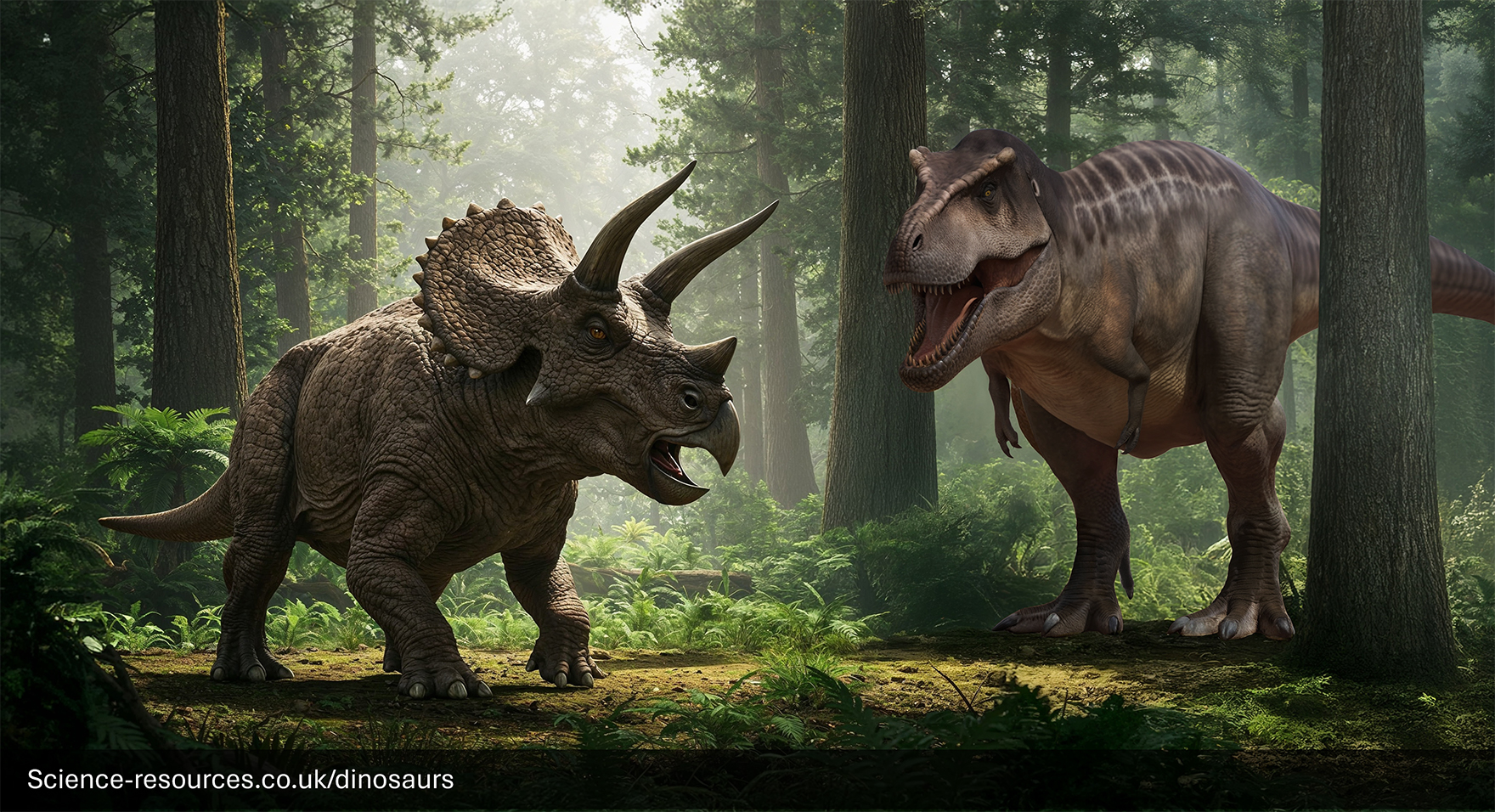

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
T-Rex was an apex predator, likely employing ambush tactics. Its powerful legs allowed for bursts of speed, and its massive jaws, filled with banana-sized teeth, delivered devastating bites capable of crushing bone. Evidence suggests it preyed on large herbivores like Triceratops and Edmontosaurus. Whether it was solely a predator or also scavenged is debated, but most agree it was an active hunter.
Jurassic Park's Tyrannosaurus
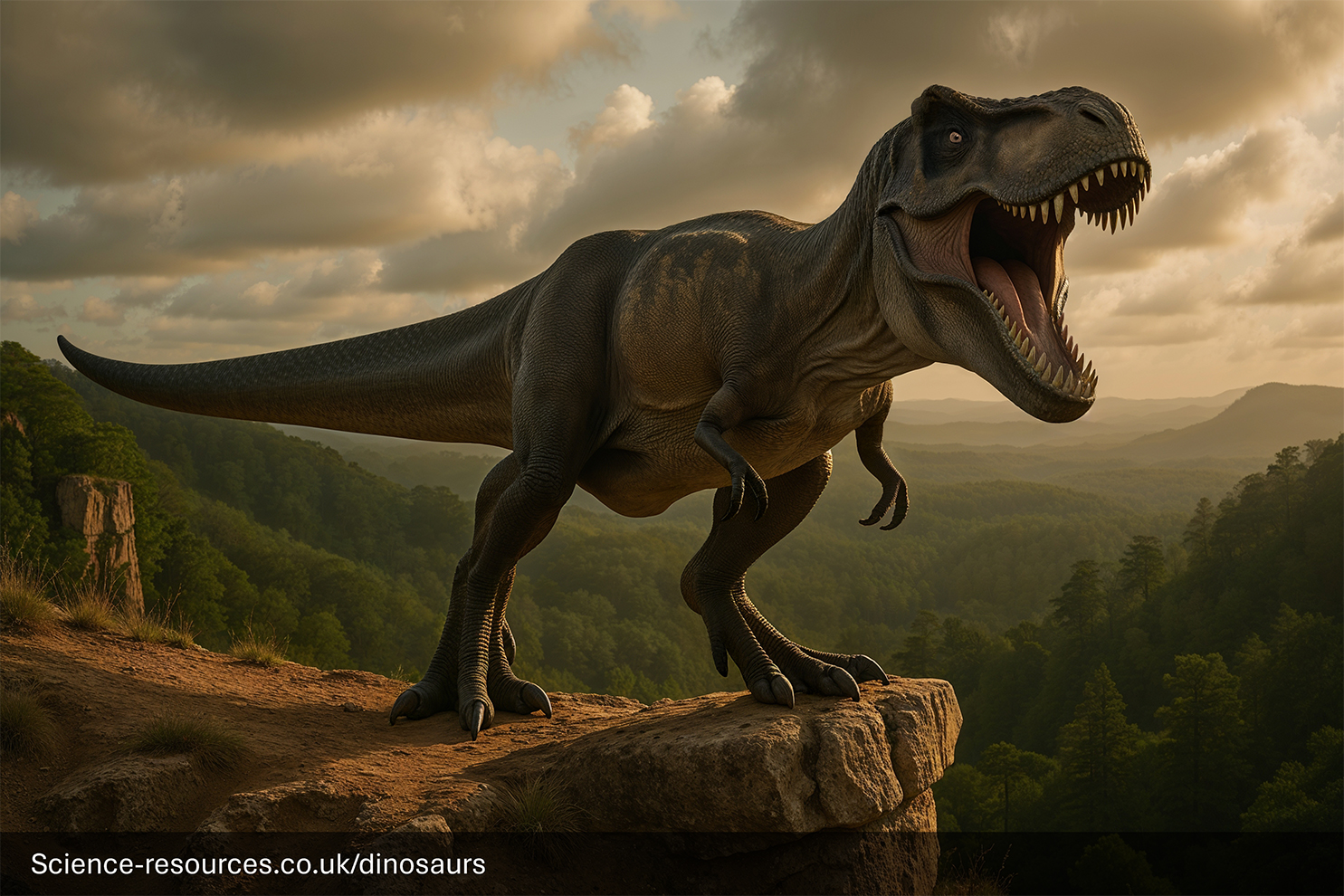

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
The T-Rex in "Jurassic Park" became an instant icon. While thrilling, it had some inaccuracies. Its vision was depicted as movement-based ("Don't move!"), but scientific evidence suggests T-Rex had excellent binocular vision. Its roar was also a sound design creation, as we don't know what it truly sounded like. However, the film captured its immense size and terror effectively.
What Did Tyrannosaurus Look Like?

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
T-Rex had a massive head with a wide gape, powerful neck muscles, and a bulky body. Its forelimbs were tiny with two functional digits, while its hind limbs were long and powerful. A long, heavy tail acted as a counterbalance. Skin impressions show scaly skin, though some theories suggest juveniles might have had feathers.
How Unique Was Tyrannosaurus?
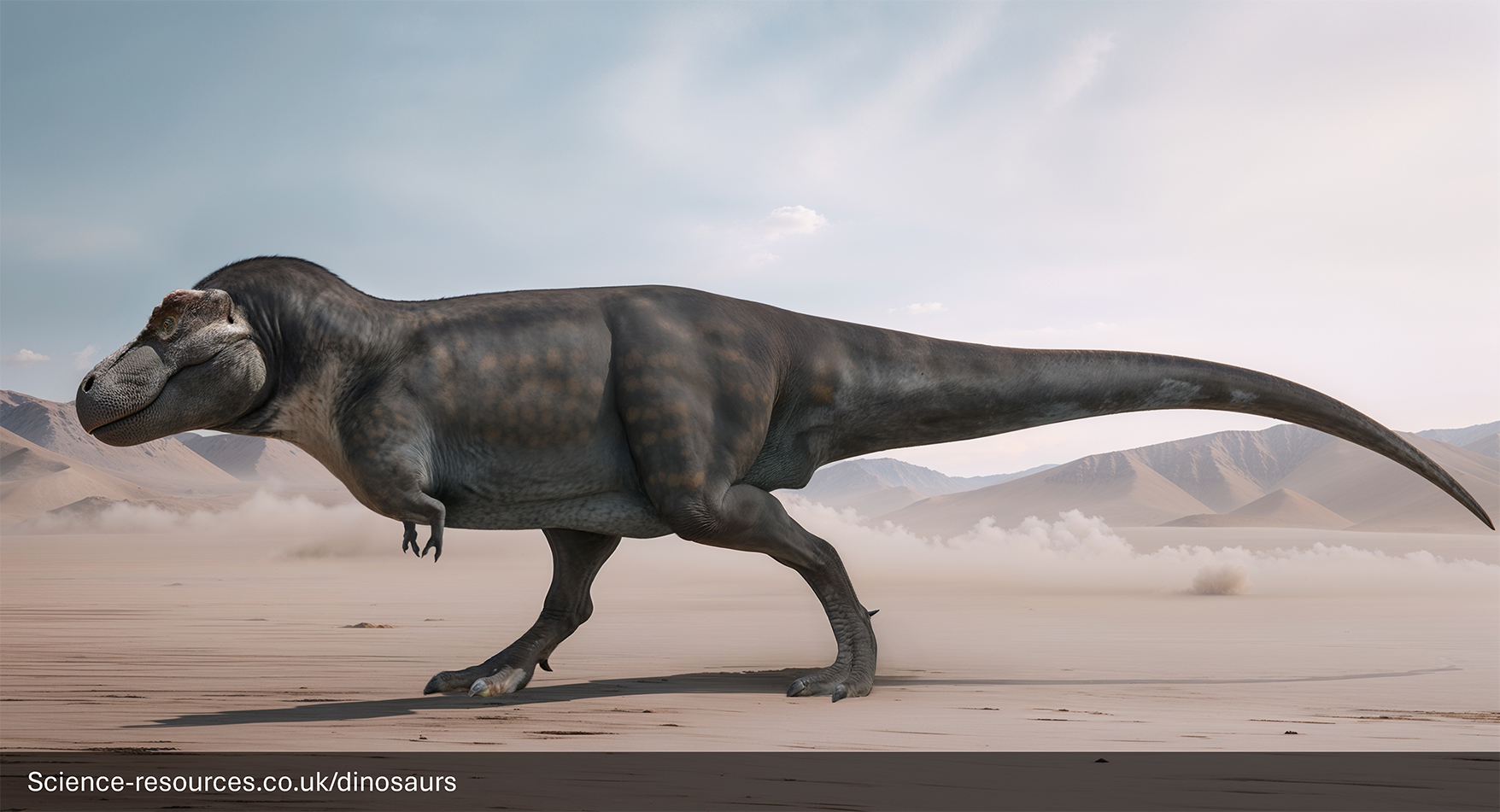

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
T-Rex was unique for its combination of immense size, incredibly powerful bite force (among the strongest of any land animal), relatively large brain for a dinosaur of its size, and keen senses, including excellent vision and smell. Its disproportionately small arms also make it distinctive among large theropods.
How Fast Could Tyrannosaurus Move?
Estimates for T-Rex's top speed vary. Early ideas suggested high speeds, but modern biomechanical studies, considering its massive weight and leg structure, point to a more moderate pace, likely around 10-25 mph (16-40 kph). This was still fast enough to pursue its likely prey but not the cheetah-like speeds once imagined.
How Smart Was Tyrannosaurus?
For a dinosaur, T-Rex was relatively intelligent. Its encephalisation quotient (EQ), a rough measure of intelligence based on brain-to-body size, was higher than many other large theropods. It had large olfactory bulbs (indicating a good sense of smell) and well-developed optic lobes, suggesting sophisticated sensory processing necessary for a predator.
Fossil Discoveries
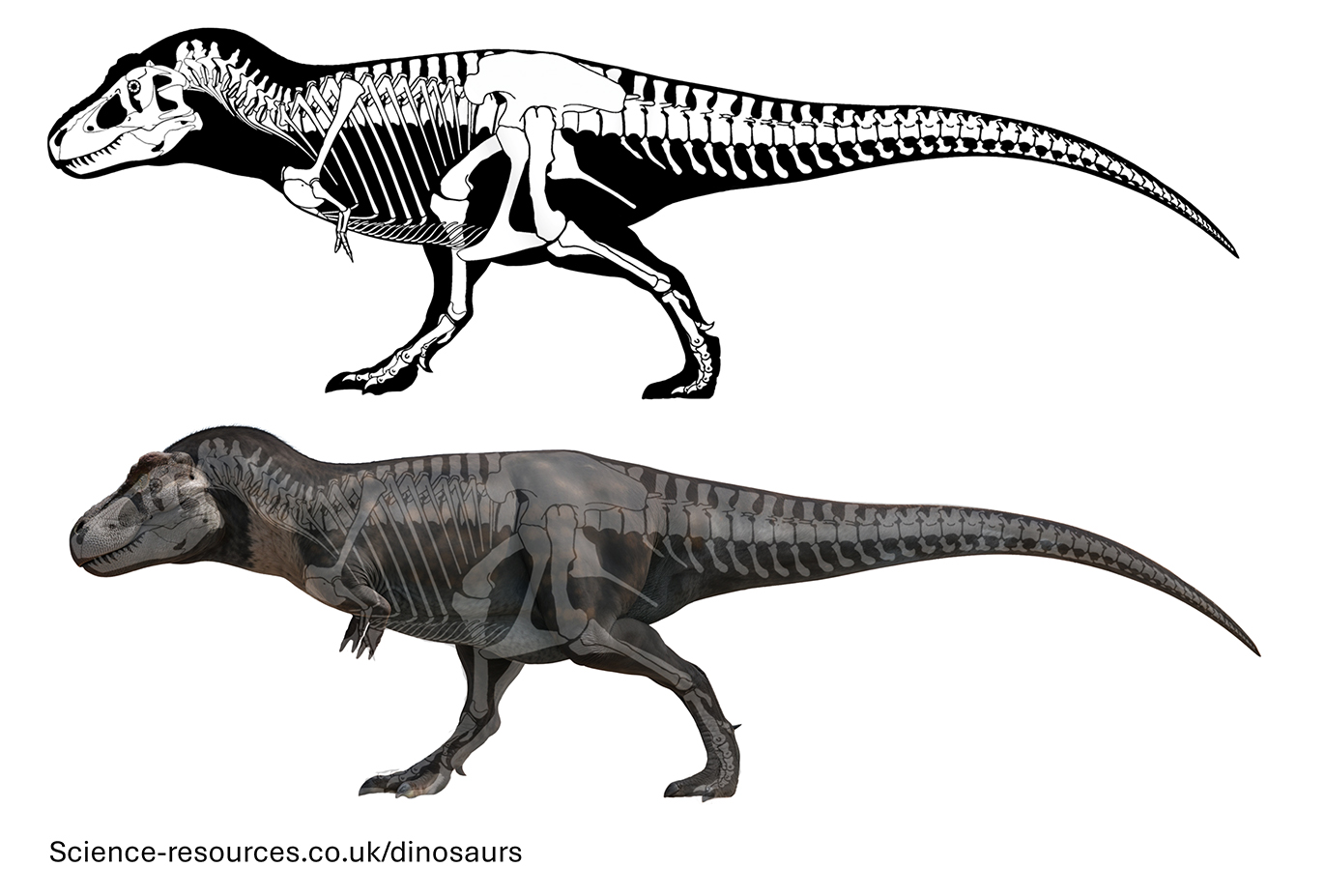
Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
Numerous T-Rex fossils have been found in western North America, from Alberta, Canada, down to Texas, USA. Famous specimens include "Sue" at the Field Museum in Chicago (one of the most complete), "Stan" (now privately owned), and "Scotty" (Royal Saskatchewan Museum). These discoveries have provided immense insight into T-Rex anatomy, growth, and behavior.
Dinosaur Family Tree
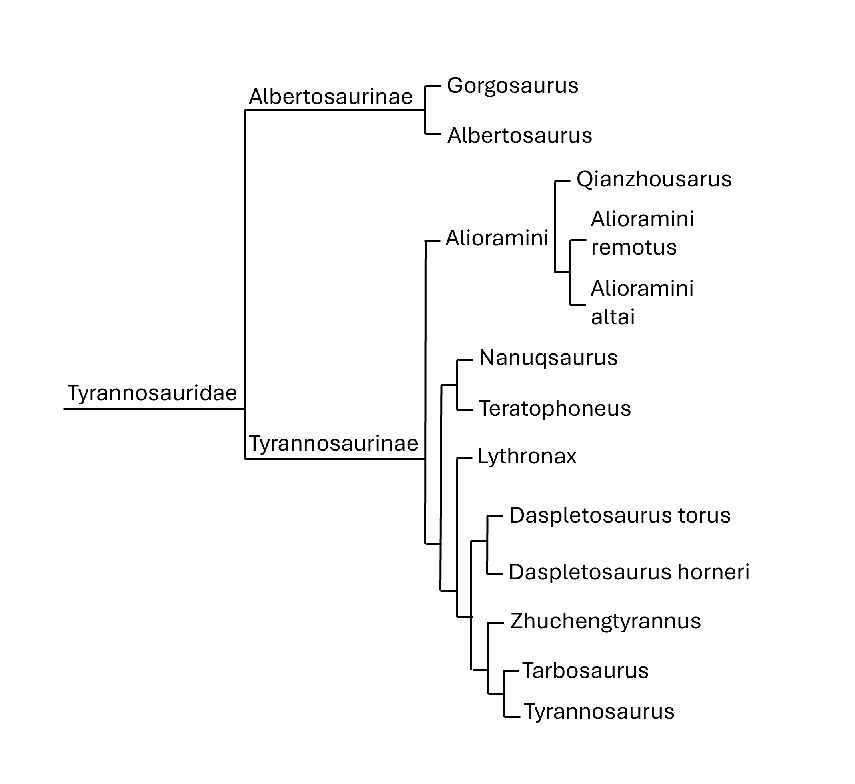
Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
Tyrannosaurus Rex belongs to the family Tyrannosauridae, which is part of the larger group Theropoda (bipedal, mostly carnivorous dinosaurs). Other tyrannosaurids include Albertosaurus, Gorgosaurus, and Tarbosaurus. Tyrannosaurids evolved from smaller ancestors and became the dominant large predators in North America and Asia during the Late Cretaceous.
How Did Tyrannosaurus Move?
T-Rex was a biped, walking on its two powerful hind legs. Its body was held horizontally, with its long, heavy tail acting as a counterbalance to its massive head. Studies of its tracks and skeletal structure suggest a relatively efficient walking gait for its size, though running would have been energetically expensive.
Features and Survival
T-Rex's survival was ensured by a suite of adaptations: bone-crushing bite to maximize food from kills, keen senses (smell and vision) to locate prey, robust build to withstand struggles, and relatively large brain for complex predatory behaviors. Its size alone would have deterred most other predators.
Changing Perceptions

Image source: https://science-resources.co.uk/KS2/Dinosaurs/Tyrannosaurus.html
Our understanding of T-Rex has evolved. Early depictions showed it as a slow, tail-dragging behemoth. Modern research portrays a more agile, dynamic animal with a horizontal posture. Debates continue on topics like its top speed, whether it was feathered, and the exact nature of its predatory behavior (hunter vs. scavenger).







